Price-Watch’s most active coverage of 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid price assessment:
- IG (99% min) FOB Nagoya, Japan
- IG (99% min) CIF_Haiphong (Japan), Vietnam
- IG (99.5% min) FOB Klang, Malaysia
- IG (99.5% min) CIF_Jakarta (Malaysia), Indonesia
- IG (99.5% min) FOB Hamburg, Germany
- IG (99.5% min) CIF_Houston (Germany), USA
- IG (99.5% min) CIF_Mersin (Germany), Turkey
- IG (99% min) CIF_Nhava Sheva (Japan), India
- IG (99.5% min) FOB Gothenburg, Sweden
2-Ethyl Hexanoic Acid Price Trend Q3 2025
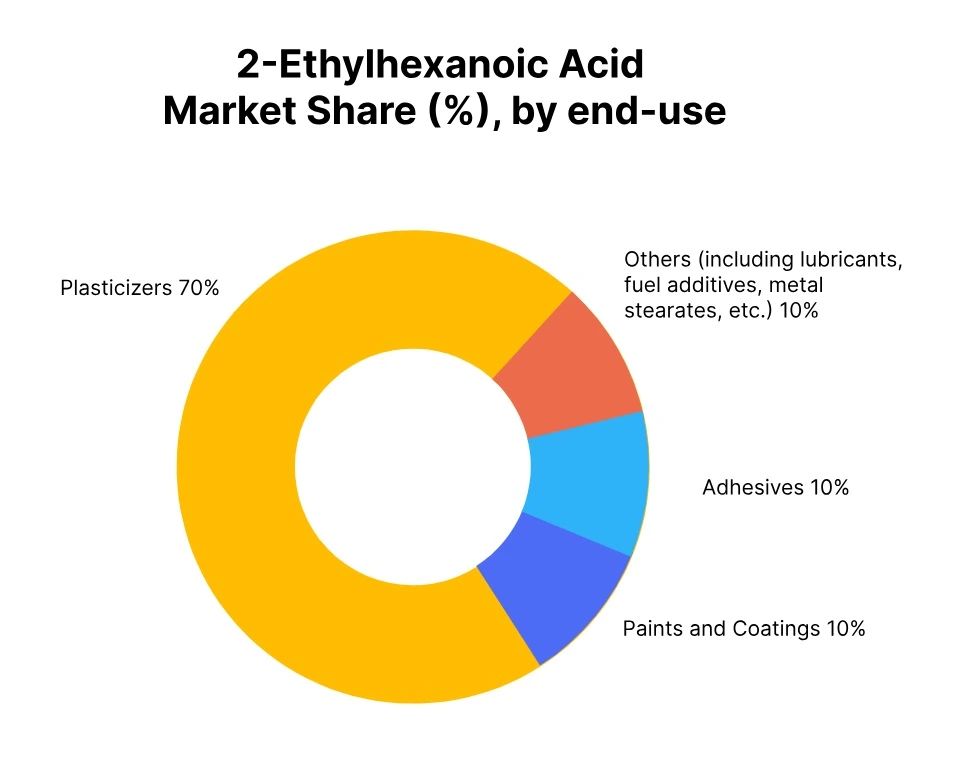
In Q3 2025, the global 2-EHA price trend showed mixed results, with declines observed in several regions and modest increases in a few others. The overall demand for 2-EHA softened due to slower industrial activity in key sectors such as plasticizers, paints and coatings, adhesives, construction, and automotive. As a result, 2-EHA prices dropped in markets like Japan, Malaysia, and Indonesia, reflecting weaker consumption across these industries.
However, regions like Sweden and India saw slight price increases, indicating more stable demand. 2-EHA prices in September 2025 continued to reflect a general global slowdown, with subdued industrial activity contributing to the price declines.
Japan: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Export prices FOB Nagoya, Japan, Grade- Industrial Grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in Japan decreased by 2.4%, reaching 1144 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The decline was primarily driven by weaker demand in key industries such as automotive and construction, both of which experienced lower production during this period. The 2-EHA price trend in Japan followed the global pattern of reduced consumption, particularly in the plasticizers and paints and coatings sectors.
Despite a stable supply, 2-EHA prices in September 2025 in Japan reflected minimal price recovery due to the sustained downturn in industrial activity. Overall, the lack of demand growth across these critical sectors contributed to the continued price decline in Japan.
Malaysia: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Export prices FOB Klang, Malaysia, Grade- Industrial Grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in Malaysia saw a significant 5.4% decrease, which dropped to 1148 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The reduction was largely due to soft demand from key industries, including plasticizers, paints and coatings, and automotive. The 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid price trend in Malaysia was heavily influenced by a global slowdown, with weaker consumption of 2-EHA in flexible PVC applications and coatings.
As a result, 2 Ethyl hexanoic Acid prices in September 2025 in Malaysia remained subdued, reflecting the continued lack of significant demand recovery. The lower demand from these industries meant that prices stayed at a lower level throughout the quarter, contributing to the overall price decrease.
Sweden: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Export prices FOB Gothenburg, Sweden, Grade- Industrial Grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in Sweden increased by 1.0%, reaching 1224 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The slight increase was supported by relatively stable demand in the construction and automotive sectors, which continued to show moderate activity despite global slowdowns. The 2-EHA price trend in Sweden was more positive compared to other regions, as the ongoing infrastructure projects and steady consumption in plasticizers helped to stabilize prices.
As a result, 2-EHA prices in September 2025 in Sweden were slightly higher than the previous quarter. This positive movement indicated a more resilient market in Sweden, where localized demand was less affected by the global economic downturn.
Germany: 2-Ethylhexanoic Export prices FOB Hamburg, Germany, Grade- Industrial Grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in Germany decreased by 1.5%, reaching 1246 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The price reduction was largely due to weaker demand from the automotive and plasticizer industries, which were affected by slower production and consumption. The 2-EHA price trend in Germany reflected a general industrial slowdown, with reduced activity in key sectors such as construction and coatings.
Despite stable supply, 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid prices in September 2025 in Germany showed continued weakness as industrial demand remained muted. The lack of significant recovery in demand across multiple sectors led to the downward pressure on prices throughout the quarter.
India: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Import prices CIF Nhava Sheva, India, Grade- Industrial grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in India experienced a slight 0.3% increase, reaching 1201 USD/MT in Q3 2025. This modest increase in 2-EHA prices was driven by relatively steady demand from the plasticizers and paints and coatings sectors, although the automotive industry remained weak. The 2-EHA price trend in India showed resilience in specific markets, despite the broader global slowdown.
2-EHA prices in September 2025 in India reflected this regional stability, as plasticizers demand remained stable, and the impact of the weaker automotive sector was less pronounced. The slight price increase indicated a modest recovery in India’s demand despite global challenges.
Vietnam: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Import prices CIF Haiphong, Vietnam, Grade- Industrial grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices In Vietnam decreased by 2.3%, falling to 1194 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The reduction was primarily driven by weaker demand from the plasticizers and paints and coatings sectors, which saw lower activity amid slower construction and automotive production. The 2-EHA price trend in Vietnam mirrored the global slowdown, with reduced consumption from key downstream industries.
2 Ethyl hexanoic acid prices in September 2025 in Vietnam remained lower than earlier in the quarter, as the market continued to feel the impact of reduced industrial output. The price decline reflected the ongoing struggles in these critical end-use sectors.
Indonesia: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Import prices CIF Jakarta, Indonesia, Grade- Industrial grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2 EHA prices in Indonesia saw a sharp 5.1% decrease, dropping to 1182 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The primary cause of this decline was weak demand in the plasticizers, paints and coatings, and automotive sectors. The 2 EHA price trend in Indonesia was significantly impacted by lower consumption in these industries, which are traditionally strong consumers of 2-EHA.
2-EHA prices in September 2025 in Indonesia were notably lower, reflecting the continued weakness in production and consumption. The reduction in industrial activity across key sectors led to the overall price decline throughout the quarter in Indonesia.
USA: 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid Import prices CIF Houston, USA, Grade- Industrial grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in the USA fell by 1.9%, reaching 1344 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The decline was attributed to reduced demand from sectors such as automotive and construction, which experienced production delays and lower sales. However, the 2 EHA price trend in the USA remained relatively stable in some areas, as the plasticizers market continued to see steady consumption.
2-EHA prices in September 2025 in USA were slightly lower compared to earlier in the quarter, reflecting slower growth in demand across key sectors. The overall market showed a modest decline in prices, which followed the global downturn in industrial activity.
Türkiye: 2-Ethyl hexanoic Acid Import prices CIF Mersin, Türkiye, Grade- Industrial grade (99% min, 99.5% min).
2-EHA prices in Türkiye decreased by 1.4%, reaching 1310 USD/MT in Q3 2025. The reduction in prices was due to weaker demand in the automotive and construction sectors, which saw lower activity during this period. The 2 ethyl hexanoic acid price trend in Türkiye mirrored the global slowdown, with decreased consumption in major industries like plasticizers and paints.
2-EHA prices in September 2025 in Türkiye were lower than in the previous quarter, following the overall market trend of reduced demand. The decline was mainly driven by reduced production and consumption in downstream industries, contributing to the overall price decrease.