Price-Watch’s most active coverage of Calcium Carbide price assessment:
- Size 50-80 mm FOB Shanghai, China
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Bangkok_China, Thailand
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Manila_ China, Philippines
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Apapa_China, Nigeria
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Alexandria_China, Egypt
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Jeddah_China, Saudi Arabia
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Port of Singapore_China, Singapore
- Size 50-80 mm CIF Nhava Sheva_China, India
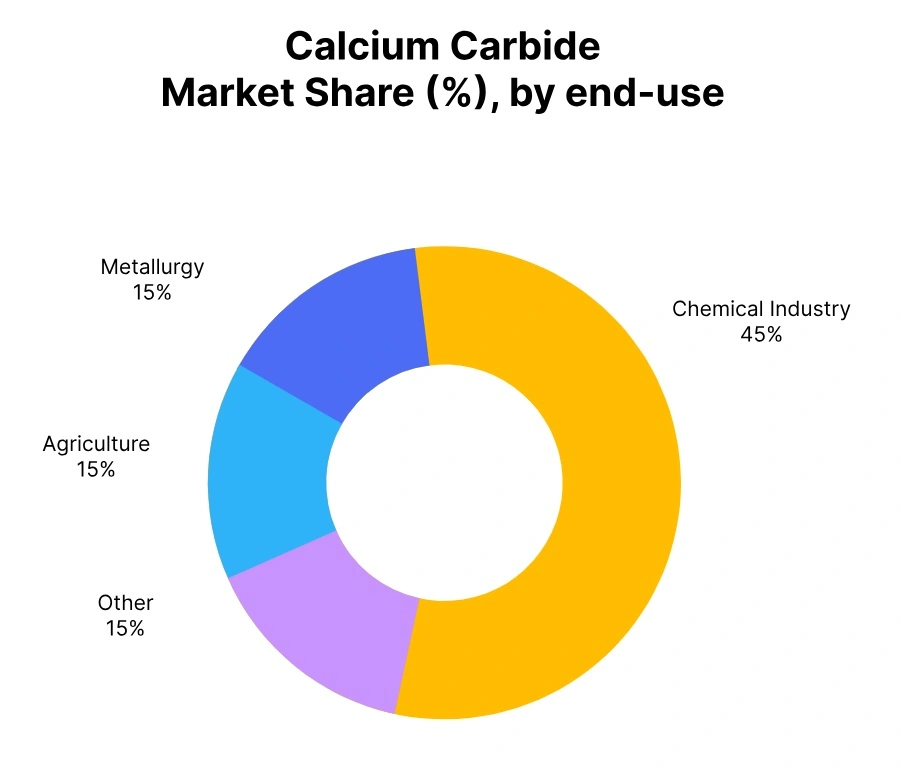
Calcium Carbide Price Trend Q3 2025
In Q3 2025, Calcium Carbide prices showed varied trends across regions. China recorded a 0.5% decline, moderating from the 1.4% drop in Q2. Thailand saw a marginal 0.1% decrease, while the Philippines experienced a sharp 5% fall due to excess inventory and weak demand. Nigeria registered a solid 3% increase, driven by strong steel and agriculture demand. Egypt posted a 1% decline amid weak industrial activity.
Saudi Arabia noted a 1% rise, supported by steady steel and chemical consumption. Singapore witnessed a 1% drop due to oversupply and subdued demand. India saw a 3% increase, backed by a rebound in steel and agriculture sectors. Overall, Calcium Carbide price trends reflected regional disparities influenced by industrial performance and trade dynamics.
China: Calcium Carbide Export prices FOB Shanghai, China, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
In the third quarter of 2025, China’s calcium carbide price trend has decreased slightly by 0.5%, showing signs of stabilization after prior continuous declines. Demand from the chemical, steel, and agriculture industries has remained stable, but not very strong, as domestic consumption has grown higher, but remains below the previous year’s levels while having reduced inventories.
Exports have continued to be limited due to declining global steel production and a reduction in fertilizer production. Seasonal farm activities have helped provide some support, but oversupply in some provinces has continued to keep pressure on prices. Calcium carbide prices in China witnessed steadiness going into September 2025, but caution remains on the buyer side with transaction activity below normal and primarily driven by need-on demand basis.
Thailand: Calcium Carbide Import prices CIF Bangkok Thailand, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
According to PriceWatch, During Q3 2025, Calcium carbide price in Thailand recorded a slight decline of 0.1% compared to Q2. The calcium carbide price trend in Thailand remained relatively stable despite slowdowns in the chemical and steel industries. Import volumes from China remained consistent, though local consumption weakened slightly amid reduced output in the metallurgy sector.
End-use industries, especially in agriculture, showed limited buying interest due to oversupplied inventories from the previous quarter. In Thailand, Calcium Carbide price in September 2025 indicated a flat trajectory with market participants adopting a wait-and-see approach amid uncertain economic signals and subdued industrial activity.
Philippines: Calcium Carbide import prices CIF Manila, Philippines, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
In Q3 2025, Calcium Carbide price in the Philippines experienced a notable 5% drop from the previous quarter, marking one of the steepest declines in the region. The calcium carbide price trend in the Philippines was impacted by lower downstream consumption in the chemical and agricultural sectors. Excess inventory carried forward from Q2, coupled with sluggish import demand, weighed heavily on prices.
Importers were cautious amid currency fluctuations and weaker regional demand. In Philippines, Calcium Carbide price in September 2025 reflected continued softness as buyers prioritized destocking over fresh purchases, keeping overall trade volumes restrained throughout the quarter.
Nigeria: Calcium Carbide import prices CIF Apapa, Nigeria, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
In Q3 2025, Calcium Carbide price in Nigeria saw a solid 3% increase over the previous quarter. The calcium carbide price trend in Nigeria was buoyed by a resurgence in steel and metallurgy operations and increased agricultural activities that boosted local demand. Imports from China remained consistent, but logistical challenges and port delays caused intermittent tightness in supply.
The chemical industry also played a supportive role in driving procurement during peak production periods. In Nigeria, Calcium Carbide price in September 2025 reflected bullish sentiment, as end-users rushed to replenish stocks in anticipation of further price hikes in the following quarter.
Egypt: Calcium Carbide import prices CIF Alexandria, Egypt, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
During the third quarter of 2025, Calcium carbide price trend in Egypt have dipped by approximately 1% compared to last quarter, signalling a mildly weak market tone. Demand from the metallurgy and chemical sectors remains weak, contributing to overall market softening. Import levels from China have remained steady, but domestic end-user demand has been muted and has prevented prices from increasing.
Agricultural end-user demand remains relatively unchanged, which has been an additional factor weighing down demand. Calcium carbide price in Egypt is minimal as of September 2025, with traders carrying low inventories and buyers unwilling to purchase due to macroeconomic uncertainty. The market remains quiet, influenced by caution, rather than momentum.
Saudi Arabia: Calcium Carbide Import prices CIF Jeddah Saudi Arabia, Grade Size 50-80 mm.
In the third quarter of 2025, the price of Calcium Carbide in Saudi Arabia rose by 1% compared to the previous quarter. The calcium carbide price trend in Saudi Arabia benefitted from increased consumption in steel manufacturing and consistent purchase levels of the chemical industry. Imports from China improved slightly in view of a creeping increase in demand from end use applications.
The agriculture sector saw moderate activity but steady operating conditions in steel and metallurgical applications have been needed to underpin the prices. The price of Calcium Carbide in September 2025 showed stable conditions in Saudi Arabia with participants’ optimism for further demand recovery in the fourth quarter.
Singapore: Calcium Carbide Import prices CIF Port of Singapore, Grade- Size 50-80 mm.
In Q3 2025, Calcium Carbide prices in Singapore have slipped by around 1% from the previous quarter, showing signs of weaker demand in the market. Consumption from the chemical and agriculture sectors has stayed muted, keeping the overall tone subdued. Imports from China have moved normally, but higher inventories have reduced fresh buying from downstream users.
The steel industry has also been running at lower capacity, adding to the slowdown. By September, Calcium carbide prices in Singapore have reflected this cautious sentiment, with traders trimming offers to keep sales moving. Recovery has been limited so far, as the market continues to adjust to slower activity and steady supply.
India: Calcium Carbide import prices CIF Nhava Seva, India, Grade- Size 50-80 mm.
In Q3 2025, Calcium Carbide prices in India have shown a modest upward move, rising about 3% from the previous quarter. The increase has been supported by renewed demand from the steel and metallurgy sectors, along with gradual restocking by downstream buyers in the chemical and agriculture industries. Imports from China have remained slow through the early part of the quarter but have improved later as port operations normalized, helping stabilize overall supply.
Toward the end of Q3, stronger buying activity has lifted sentiment slightly. Calcium Carbide prices in India have reflected a steady tone, with buyers adapting to revised cost levels and looking ahead to firmer industrial output in the coming months. The market has stayed firm but measured, showing confidence built more on recovery than on momentum.