The hot rolled coil (HRC) steel market in 2025 is at the center of global industrial shifts, where trade policy changes, fluctuating demand, and evolving production dynamics are reshaping supply chains and competitiveness. From India’s rising domestic appetite to China’s export recalibration, and from Europe’s cost challenges to the USA’s push for resilience, the market reflects both volatility and opportunity. This article explores how these forces are converging across key steel-producing hubs and what the outlook holds for the remainder of the year.
The global HRC steel market is marked by steady growth, driven by robust demand across multiple industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing. As one of the most versatile products, hot-rolled coils are utilized in a wide range of applications, from structural components in buildings and infrastructure to auto body parts and industrial machinery. As the global economy slowly recovers from post-pandemic and other systemic slowdowns, the demand for HRC continues to rise, prompting manufacturers to adjust their strategies.
Resilient Growth Amidst Challenges in India
India stands as one of the world’s largest producers and consumers of steel, a sector that continues to grow due to the country’s expanding infrastructure and automotive sectors. Hot-rolled coils (HRC), a key component in steel production, are in high demand, driven by these sectors’ development. However, the Indian steel industry is facing significant challenges, particularly from rising imports, especially from global giants like China, South Korea, and Japan. These imports put pressure on local HRC prices and reduce the market share of domestic manufacturers.
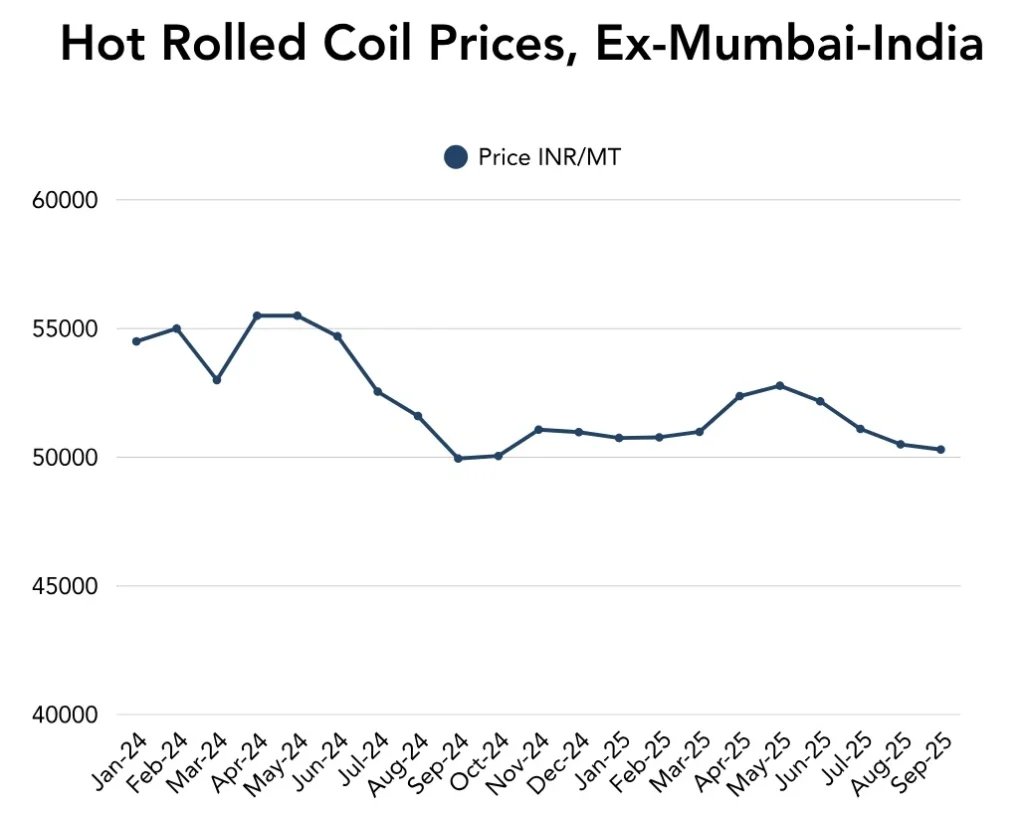
Despite India’s growing steel demand, the influx of cheap imports has become a major concern. The increased competition from overseas suppliers, especially in the wake of global HRC price fluctuations, is squeezing margins for domestic steel producers. The surge in imports, which the government has identified as a potential threat to the industry, is largely attributed to the significant price gap between foreign and domestic steel.
To shield domestic producers from unfair competition, the Indian government has recently imposed a 12% safeguard duty on imports of certain flat steel products. Industry leaders, including Naveen Jindal, president of the Indian Steel Alliance (ISA), have expressed confidence that this duty will offer the necessary protection. Jindal highlighted that while the duty may seem lower than expected, it is sufficient for now, although the industry may request adjustments if the pressure from imports continues to rise.
The safeguard duty is seen as a temporary measure to protect India’s steel producers from sudden surges in imports, which could potentially cause serious injury to local manufacturers. The Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR), operating under the Ministry of Commerce, has recommended this safeguard duty for a period of three years.
The steel industry in India is not only looking at incoming shipments, but it is also facing changing global conditions when it comes to HRC steel prices. Some of this volatility is due to production cost fluctuations around the world because demand and supply conditions are changing. Trade tensions, notably with the US, have also led to lower levels in global steel prices. These trade imbalances and issues arising from foreign sources indicate the need for strengthening domestic production within India.
In response, the Indian government is now trying to increase domestic steel production capacity making it for the long-term potential to be less dependent on imports. This will ensure a more independent source of steel production and therefore a more competitive steel industry.
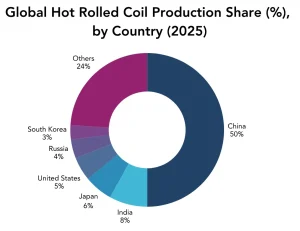
Export Surge Amid Domestic Market Challenges in China
China, the world’s largest steel producer, has witnessed significant shifts in its steel production and consumption patterns. While it remains a key player in the global HRC market, the domestic steel sector has been facing severe challenges.
The Chinese steel industry has been affected by slowing domestic demand. Key sectors like construction and automotive, traditionally heavy consumers of steel, have faced growth slowdowns. The construction sector’s slowdown is attributed to weakening real estate investment and broader economic uncertainties, with forecasts indicating a continued decline in steel consumption within this sector over the next five to ten years.
Furthermore, the Chinese government has enacted stringent environmental regulations to curb pollution, including restrictions on older, inefficient steel mills. While these moves benefit the environment, these have led to temporary shutdowns and a reduction in production capacity, putting pressure on domestic supply in the short-term.
In response to sluggish domestic demand and tighter environmental rules, China has focused on increasing its steel exports. In recent years, Chinese exporters have been leveraging the ability to produce steel at lower costs, allowing them to remain competitive in international markets despite tariff barriers. Chinese steelmakers have increasingly turned to semi-finished products, such as billets and slab steel, which face fewer trade restrictions.
Despite efforts to cut overall steel output by an estimated 5% in 2025, some regions and private mills continue production depending on profitability and demand conditions, while export volumes have surged. China’s steel exports reached record levels in the first half of 2025, driven by strong demand in Southeast Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America. However, these export dynamics are influenced by emerging anti-dumping measures and evolving trade barriers.
Oversupply and Regulatory Pressures in Europe
The goal of the European Green Deal is for Europe to achieve carbon-neutrality by 2050 and that has huge implications for steel production. Steel producers are under diligent pressure to both produce producer way and reduce carbon emissions. To facilitate this transition, the European Union has started the process of executing a Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), which places a price on carbon-intensive steel imports. This is expected to help facilitate a cleaner investment by European steelmakers, while ensuring local producers are not disadvantaged from imports produced with relatively higher carbon emissions.
Shifting Trade Policies and Domestic Production in the US
Steel prices and demand for hot-rolled coils in the U.S. market have been affected by trade policies, which have led to strong HRC price fluctuations. The Section 232 tariffs imposed on steel imports during the Trump administration redefined the steel market. The policy aimed to expand domestic steel production and protect American jobs, but the tariffs led to higher prices for imported steel and ultimately drove prices up for domestic consumers and manufacturers.
American steel manufacturers are reacting to changing market conditions by increasing production and focusing on higher quality and specialty steel products, as well as hot-rolled coils. There is also a growing focus on electric arc furnaces (EAFs), which provide a healthier and more efficient process for producing steel.
In addition to production changes, the U.S. market is feeling pressure from higher raw material costs and active trade negotiations with significant trading partners, including China and Canada. The U.S. government’s approach to tariffs and trade agreements will continue to impact competitive conditions in the U.S. steel market.
The Road Ahead
The global hot-rolled coil (HRC) market in 2025 is entering a storm of transformation, where trade policy, technology shifts, and sustainability pressures are rapidly redrawing competitive lines. India’s safeguard duties on flat steel are a microcosm of this struggle balancing protection from cheap imports with the need to stay aligned to global shifts in production, trade, and emissions standards.
Yet India is not alone: China recalibrates exports, Europe battles cost and carbon rules, and the U.S. doubles down on resilience. As steel demand keeps climbing worldwide, regional responses will shape the industry’s future, forcing both governments and producers to embrace flexibility, innovation, and strategy to thrive in this volatile new era.

