Price-Watch’s most active coverage of Propylene price assessment:
- Polymer Grade FOB Busan, South Korea
- Polymer Grade CIF Shanghai (South Korea), China
- Refinery Grade FOB Houston, USA
- Refinery Grade CIF Barranquilla (USA), Colombia
- Refinery Grade CIF Manzanillo (US), Mexico
- Polymer Grade FD Rotterdam, Netherlands
- Polymer Grade FD Hamburg (Netherlands), Germany
- Polymer Grade FD Antwerp, Belgium
- Polymer Grade FOB Laem Chabang, Thailand
- Polymer Grade CIF Jakarta (Thailand), Indonesia
- Polymer Grade CIF Port of Singapore (Thailand), Singapore
- Polymer Grade CIF Port Kelang (Thailand), Malaysia
- Polymer Grade FOB Tokyo, Japan
- Polymer Grade FD Genoa, Italy
- Polymer Grade FD Le Havre, France
- Polymer Grade FOB Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- Polymer Grade FOB Kaohsiung , Taiwan
- Polymer Grade CIF Nhava Sheva (Thailand), India
- Polymer Grade FOB Houston, USA
- Polymer Grade CIF Manzanillo (US), Mexico
- Polymer Grade CIF Barranquilla (USA), Colombia
Propylene Price Trend Q3 2025
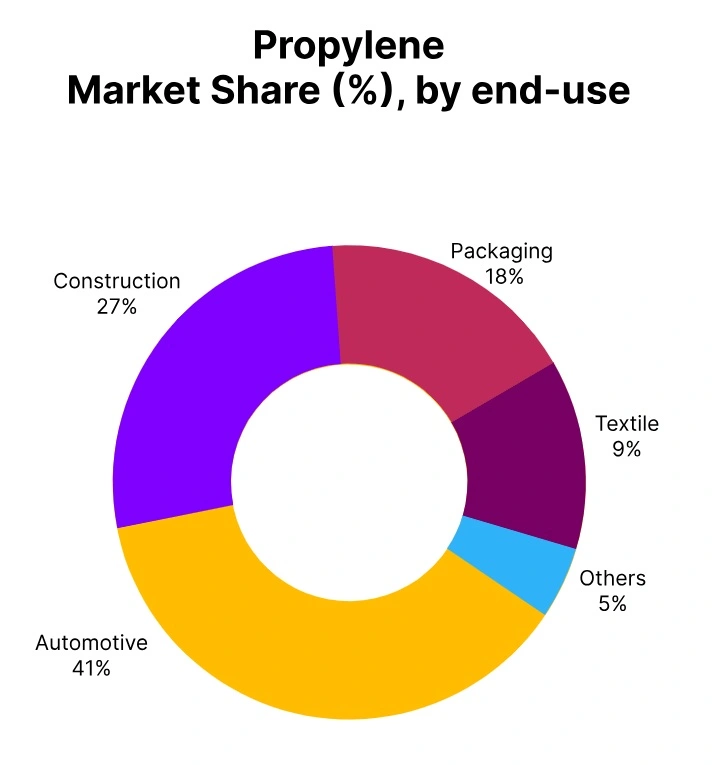
During the third quarter of 2025, the global Propylene market varied significantly from region to region. Western markets such as Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands saw considerable Propylene price trend declines due to weak demand (across automotive, packaging, and construction), thus leading to cautious procurement and oversupply.
European producers sustained steady output levels amid weak industrial activity and high energy prices. Similarly, the Asia-Pacific markets (South Korea, India) experienced downward pressure due to weak demand downstream and increased competition, in addition to freight costs impacting Overall prices.
The U.S. and North America also saw moderate weakness due to the softness of exporter demand as well as saturation of supply (though recently there has been upwards pressure in the Texas and Gulf Coast.). Generally speaking, the market was reasonably balanced sustained feedstock availability, some moderation in freight costs, and regional consumption variance were underpinning factors. Supply chain fundamentals and regional demand downstream continued to be the pricing leads during the quarter.
South Korea: Propylene Export Price from South Korea, Polymer Grade FOB Busan.
In South Korea, Propylene prices exhibited a small degree of softness in Q3 2025, due to balanced supply and moderate demand on the part of the downstream polypropylene and acrylonitrile sectors in Northeast Asia. Propylene FOB Busan price trend were in the USD 730–770/metric ton range, indicating a quarterly price reduction of 1.22%.
Cracker run rates remained steady, with no significant outages. Propylene prices in South Korea decreased by 2.95% in September 2025 from the prior month, reflecting cautious buying in the context of weak regional polymer demand.
The price developments for Propylene in South Korea have reflected limited directional movements in Naphtha feedstock costs. Buyers from China and Southeast Asia were selectively procuring in concert with weak industrial activity. Overall, the mood in the market is cautious with steady supply support, but soft demand.
China: Propylene Import Price in China from South Korea, Polymer Grade CIF Shanghai (South Korea).
In Q3 2025, Propylene prices in China showed a downward trend during the quarter with CIF Shanghai prices at USD 750–800/mt, a 1.49% drop from the previous quarter. Freight rates eased slightly, creating some marginal landed cost relief. Year-on-year, in September 2025, Propylene prices are down 2.47% from August due to selective purchasing as local PDH capacity continues to ramp up. Propylene Price trends in China were largely driven by prolonged weak demand from both polypropylene and propylene oxide producers.
Downstream consumption has been weak for an extended period, and this was despite some perception of cost advantage to process. Importers preferred to purchase supplies from quality origin suppliers, however, China’s move for self-sufficiency continued to suppress any minor uptick. The overall market sentiment is generally stable but cautious as the balance shifts towards local production gradually.
Netherlands: Propylene Export Price from Netherlands, Polymer Grade FD Rotterdam.
In Q3 2025, Propylene price trend in Netherlands underwent a notable reduction as European demand from the polymer, resin, and chemical derivative sectors remained weak (FD Rotterdam, USD 840–930/ Metric ton), indicating a quarter-over-quarter decline of 7.99%. Downstream converters continued to operate at diminished rates with a declining construction and automotive output.
In September 2025, Netherlands Propylene prices fell 2.35% from the previous month, while consumption remains restrained and the downward trend was maintained. The Netherlands Propylene price trend was also influenced by stable feedstock Naphtha price levels and above-average energy costs.
The overall supply was abundant from integrated petrochemical complexes ensuring no prices were corrected upwards immediately. Overall, market conditions remain oversupplied with limited near-term price support or upside.
Germany: Propylene Domestically Traded Price in Germany, Polymer Grade FD Hamburg (Netherlands).
During Q3 2025, the Propylene trend price in Germany was downwards, in line with broader weakness within the European market. The FD Hamburg price range was USD 870–970 metric ton for the quarter, reflecting a decrease of 7.74% from the previous quarter. Demand levels from polypropylene, resins, and other industrial chemicals did not materially shift during the quarter.
In September 2025, Propylene prices in Germany dipped by 2.79% versus the previous month, attributed to continued cautious purchasing activity by converters, who have yet to see an uptick in demand tied to new industrial output.
Furthermore, the overarching Propylene price trend in Germany has reflected steady supply levels from producers both domestic and in neighbouring countries, impeding upward price recovery. Logistics and handling costs exhibited marginal variations. Overall, the market remains firmly bearish, with pricing under pressure from limited demand levels that maintain consistent availability.
Belgium: Propylene Domestically Traded Price in Belgium, Polymer Grade FD Antwerp.
During the third quarter of 2025, Propylene price in Belgium experienced a consistent decline, due to ineffective demand from the packaging, automotive, and construction industries. Prices at FD Antwerp averaged USD 860–960 per metric ton, representing a decline of approximately 7.60% in the quarter.
Supplies from the Antwerp petrochemical complex were steady and available, but downstream converters limited their offtakes. Business activity was still weak, and Propylene prices in Belgium decreased another 2.28% from last month in the month of September 2025.
The downward Propylene price trend in Belgium was a reflection of no support for rising prices attributable to feedstock costs associated with Naphtha. European producers adjusted operating rates to respond to weak consumption signals. Overall, market sentiment remains cautious, and pricing is likely to remain under pressure in the near term.
Thailand: Propylene Export Price from Thailand, Polymer Grade FOB Laem Chabang.
In the third quarter of 2025, Propylene prices in Thailand fell sharply due to factors including soft regional demand and competition from suppliers in the Middle East and China. The price of Propylene on a free on board (FOB) basis in Laem Chabang was reported in the range of USD 710–780/metric ton, which reflects a decrease of 10.22% from the previous quarter.
The operating rates of polypropylene producers remained low and increasingly limited offtake. Propylene prices in Thailand decreased by 1.37% in September 2025 compared to August 2025 prices, continuing the bearish trend despite some slight downstream activity.
Propylene price trend in Thailand continued to be pressured by softened Naphtha costs, which did not offer much price support. Thai crackers ran at steady operating rates, however, inventories were building in the major trading hubs. Overall, sentiment in the markets continues to remain bearish, with high supply levels.
Indonesia: Propylene Import Price in Indonesia from Thailand, Polymer Grade CIF Jakarta (Thailand).
In Q3 2025, Propylene price in Indonesia decreased moderately, with CIF Jakarta prices ranging from USD 780–840 per metric ton. This price decrease reflects a quarter-over-quarter price decline of 9.52%. Freight costs remained relatively stable and helped maintain predictable landed pricing. In September 2025, the price of Propylene in Indonesia decreased 1.13% from the previous month due to limited buying interest amid muted domestic consumption.
Price trends for Propylene in Indonesia were influenced by steady supply from Thailand and softer interest from the plastics and packaging sectors. Converters maintained cautious rates of operation, and spot market activity was limited. Overall, the market remains well-supplied, and pricing is under some pressure due to oversupply in the region.
Singapore: Propylene Import Price in Singapore from Thailand; Polymer Grade CIF Port of Singapore (Thailand).
In Singapore’s Q3 2025, Propylene exhibited considerable downside pressure that saw prices (CIF Port of Singapore) in the range of USD 740–810 per metric ton, a quarterly decline of 11.09%. Freight rates fell considerably, providing substantial landed cost relief. Propylene prices in September 2025 decreased another 1.19% from the previous month, as buyers took a cautious approach in response to limited downstream activity.
The Propylene price trend in Singapore was affected by competing pricing from Thai suppliers and generally weak regional demand. Converters and buyers showed selectivity with minimal activity in the spot market. The market still appears to be oversupplied, and pricing continues to show downside pressure.
Malaysia: Propylene Import Price in Malaysia from Thailand, Polymer Grade CIF Port Kelang (Thailand).
Throughout Q3 2025, Propylene price in Malaysia exhibited a decreasing trend, with CIF Port Kelang fees between USD 760–830 metric ton, for an overall decline of 10.00%. Freight costs also experienced a slight decline, contributing to a reduced overall landed price. In September 2025, propylene price in Malaysia declined by 1.15% month over month, suggesting soft demand persisted in downstream plastics and industrial goods.
Propylene price trends in Malaysia were driven by steady supplies from Thailand, combined with cautious procurement from local converters. The market sentiment remained subdued, reporting minimal spot activity. Overall, the market remains well-supplied with pricing pressure from regional excess supply.
Japan: Propylene Export Price from Japan, Polymer Grade FOB Tokyo.
In Q3 2025, Propylene prices in Japan fell slightly, partly due to sluggish regional demand and further import competition from Middle Eastern and Chinese suppliers. The price for Propylene delivered on the FOB Tokyo ranged from USD 740 to 760 per metric ton, which was a drop of 4.03% from the last quarter.
Domestic cracker rates were steady, with limited export volumes traded due to a softened buying interest. In September 2025, Propylene prices in Japan decreased 1.31% from the previous month, again reflecting a generally moderate decrease.
The Propylene price trend in Japan was slightly affected by steady costs for Naphtha feedstock. Japanese producers also kept the price at competitive levels to secure contracts, while converters, downstream, were cautious in their buying. Overall, market sentiment appeared weak, with limited chances in the near-term for recovery.
Italy: Propylene Domestically Traded Price in Italy, Polymer Grade FD Genoa.
During Q3 2025, the price of Propylene in Italy registered a small decline, as downstream demand from the polymer and industrial chemicals markets remained weak. FD Genoa to freight at the port of Genoa indicated a price range of USD 840–930 per metric ton – a quarterly decrease of 7.46%. Downstream converters were forced to continue to operate conservatively in light of soft industrial production output.
During September 2025, Propylene prices in Italy fell by 2.34% month-to-month, sustaining the overall bearish trend of the domestic markets. The overall Propylene price trend in Italy would remain under pressure from stable supply from domestic and neighbouring producers, while limited support was provided from feedstock Naphtha costs. Overall market conditions remained oversupplied, with Propylene continued to be pressured.
France: Propylene Domestically Traded Price in France, Polymer Grade FD Le Havre.
In Q3 2025, Propylene price in France continued to experience significant downward pressure due to a reduction of consumption from both the automotive, packaging, and construction industry. Throughout the quarter, FD Le Havre pricing found a new range of USD 940–1,100 per metric ton, for a quarterly decrease of 9.12%. French converters operated at reduced rates of capacity, minimizing offtake from both domestic sources and imports.
In September 2025, Propylene prices in France increased slightly by 0.34% from August, offering small relief in an otherwise weak domestic market. The Propylene price trends in France were contingent on limited feedstock and supporting energy costs. Sentiment continues to remain subdued overall, with continued oversupply continuing to introduce downward price pressure.
Saudi Arabia: Propylene Export Price from Saudi Arabia, Polymer Grade FOB Jeddah.
In Q3 2025, Propylene price in Saudi Arabia saw moderate downside due to soft regional demand and increased competition from Chinese and other Middle Eastern suppliers. Prices reached USD 740–780 per metric ton, with a quarterly decline of 5.83%.
Cracker operations in Jubail and Yanbu were sustained at the high-utilization rates, ensuring uninterrupted supply levels. In September 2025 Propylene prices in Saudi Arabia fell by 1.98% from the month prior, as slow buying activity persisted because of limited demand recovery.
In Saudi Arabia, the price trend of Propylene was affected by fixed costs for the use of ethane as a feedstock, allowing for a competitive price advantage. In general, the market remains balanced – prices are buoyed by reliable availability of supply but pressured by weak regional demand.
Taiwan: Propylene Export Price from Taiwan, Polymer Grade FOB Kaohsiung.
In the third quarter of 2025, Propylene price in Taiwan decreased moderately, impacted by weak buying interest in the region and competition from China and the Middle East. Propylene prices trend FOB Kaohsiung were noted at USD 750–800 metric ton and that is a quarterly decrease of 6.06%.
Downstream polypropylene producers continued to appear to be cautious in operating rates. In September of 2025, the price of Propylene in Taiwan increased slightly, rising 0.56% month-on-month, indicating slight market correction, while continuing to oversupply.
The Taiwan Propylene price trend was supported by the stable operation of crackers, and lack of volatility in Naphtha feedstock costs. Overall, the market sentiment remained weak and was characterized by limited buying activity across key trading hubs. Overall, the market remains under price pressure.
India: Propylene Import Price in India from Thailand, Polymer Grade CIF Nhava Sheva (Thailand).
According to Price-Watch, during Q3 2025, Propylene price in India declined moderately, with CIF Nhava Sheva prices ranging between USD 770–820 per metric ton, reflecting a quarterly drop of 6.69%. Freight costs rose significantly, adding upward pressure to landed prices. In September 2025, Propylene prices in India decreased by 2.53% from the previous month, indicating cautious procurement amid weak downstream demand.
The Propylene price trend in India was influenced by competitive pricing from Thai suppliers and soft demand from polypropylene and packaging sectors. Local buyers remained selective, with limited spot activity reported. Overall, market conditions remain oversupplied, with pricing under downward pressure.
USA: Propylene Export Price from USA, Polymer Grade FOB Houston.
In Q3 2025, Propylene price in USA declined notably, reflecting weaker demand from European and Latin American buyers amid global oversupply concerns. FOB Houston prices ranged between USD 720–860 per metric ton, reflecting a quarterly decrease of 8.79%. Domestic offtake remained strong, but export demand softened. In September 2025, Propylene prices in USA increased by 6.22% from the previous month, providing a temporary rebound amid tighter domestic supply.
The Propylene price trend in USA was influenced by slightly lower Propane feedstock costs. Suppliers maintained competitive pricing to secure overseas contracts. Overall, market sentiment remains mixed, with moderate upward price correction limited by global oversupply.
Mexico: Propylene Import Price in Mexico from USA, Polymer Grade CIF Manzanillo (US).
During Q3 2025, Propylene price in Mexico declined moderately, with CIF Manzanillo prices ranging between USD 780–920 per metric ton, reflecting a quarterly decrease of 8.07%. Freight costs increased marginally, contributing to higher overall expenses. In September 2025, Propylene prices in Mexico increased by 5.75% from the previous month, indicating partial recovery amid stable import supply from regular supplying nations.
The Propylene price trend in Mexico was influenced by weak downstream demand from polypropylene and automotive sectors. U.S. suppliers ensured reliable supply, while Mexican converters maintained cautious procurement. Overall, market sentiment remains cautious, with selective buying supporting minor upward adjustment in prices.
Colombia: Propylene Import Price in Colombia from USA, Polymer Grade CIF Barranquilla (USA).
According to Price-Watch, in Q3 2025, Propylene price in Colombia remained under moderate pressure, reflecting soft regional demand and global oversupply. CIF Barranquilla prices ranged around USD 824 per metric ton, reflecting steady quarterly performance. In September 2025, Propylene prices in Colombia increased by 5.58% from the previous month, reflecting improved import activity and limited domestic stock.
The Propylene price trend in Colombia was influenced by consistent supply from the U.S. Gulf Coast. Local buyers from polymer and industrial sectors maintained selective procurement amid weak overall demand. Market conditions remain stable, with pricing supported by reliable imports but tempered by limited consumption growth.