The year 2025 has brought striking changes in Acetic acid production, demand, and logistics shaped not only by technological innovation and shifting markets but also by geopolitical challenges. A key disruptor has been the prolonged political unrest in Nepal, which has severely rattled regional supply chains, including the acetic acid market. This article dives deep into current trends shaping acetic acid’s landscape, with a focused look at how Nepal’s turmoil is impacting production and logistics in the region.
Production Trends and Technological Advancements
Global Production Changes
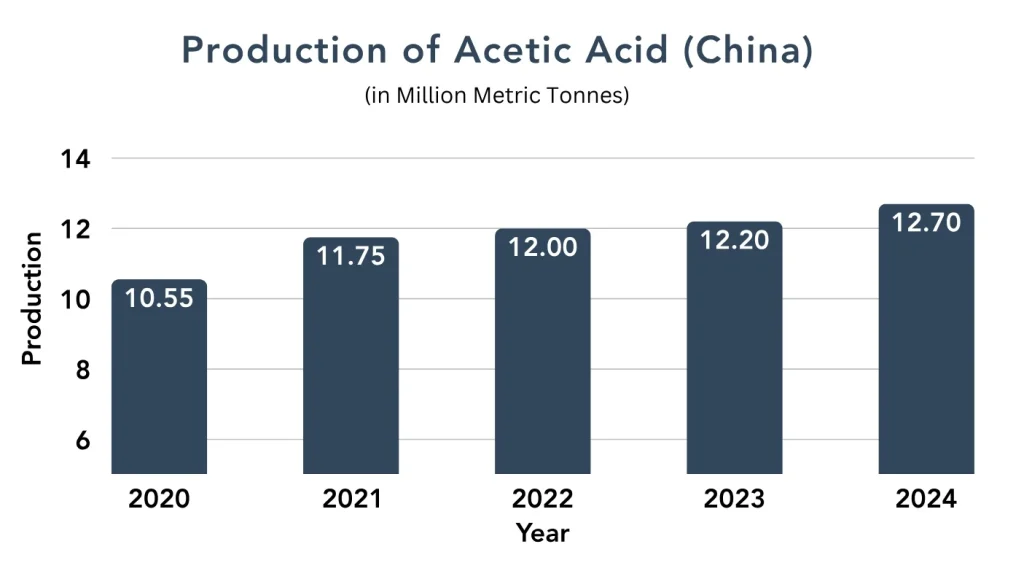
By 2025, we continue to see increases in the global production of acetic acid. China and India remain the leading countries in this production. China is the dominant producer, with approximately 60% of the global acetic acid production capacity. India has also expanded its production capacity with the growth of its industrial base in recent years. The largest demand for acetic acid is from the automotive, construction and textile industries, which produce acetic acid derivatives such as Vinyl acetate monomer (VAM).
Advancements in Technology
Over the past ten years, there have been advancements in the techniques for producing acetic acid. While carbonylation of methanol using catalysts such as rhodium or iridium is still most prevalent, especially in larger plants, alternative approaches, including the Cativa process pioneered by BP and the Monsanto process, have gained market share.
Also, there is an increased interest in bio-based production of acetic acid. Bio-based production using renewable feedstocks, like corn or sugarcane, is gaining traction as industry responds to increased sustainability pressures stemming from global markets. By 2030, bio-based production of Acetic acid is projected to have an increased share of global production consumption.
Demand Dynamics and Market Trends
Industrial Use
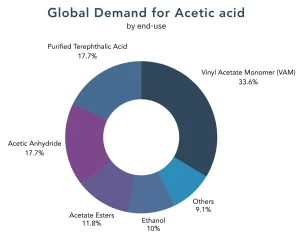
The global demand for acetic acid in 2024 was estimated to be 19.5 million metric tons, as per the latest PriceWatch data. Acetic acid is primarily utilized in the production of VAM; VAM is an important component of adhesive and paint and coating and textile production. It plays an important role in industrial applications, such as automobile manufacture (for coatings and adhesives), as well as in construction applications (paints and sealants). These applications all contribute to increased demand particularly in fast-growing industrial markets, especially between 2015 and 2020 in China and India.
Emerging Markets and New Uses
Acetic acid demand is on the rise in emerging economies in Asia, Latin America and African region. With unending urbanization and higher population density, emerging economies are starting to experience greater demand for acetic acid in areas like packaging, food preservation, agriculture and textile production. In Africa, for example, increasing demand for plastics in construction and packaging has impacted the demand for acetic acid.
In addition, acetic acid derivatives and other uses such as acetate esters and acetic anhydride are also gaining traction in new applications. Traditional uses of these derivatives include pharmaceuticals, plastics and the preservation of some foods and food items. Growth in areas related to these derivatives will spike demand for acetic acid.
Environmental Considerations
There is rising pressure on the chemical industry to meet stricter and more stringent environmental regulations around the world. Due to this, acetic acid production is moving towards more sustainable practices and methods. In particular, bio-based production processes which use renewable resources instead of fossil fuels are becoming attractive options for producers as they will reduce overall carbon emissions. European and North American based companies and producers are moving toward bio-based acetic acid production and initiating policy changes in existing regulations to clarify sustainability initiatives to meet government requirements and raise their bar on cleanliness.
There is a significant shift towards greener technologies in Asia, where traditional methods have been entrenched.
Logistics and Supply Chain Developments
Transportation and Distribution
The logistics of acetic acid (which is corrosive and, therefore, a product that requires specialized transport) have traditionally made transportation a challenge for the acetic acid industry. When contained, transported, and stored, acetic acid must be handled in a safe manner, and special equipment, transportation, and packaging must be used to keep acetic acid safe while being distributed. Over the last twenty years, improvements in packaging technology have increased the safety and efficiency of the logistics of acetic acid, which has lowered both cost and risk of loss.
Transporting acetic acid, in particular, is dependent on how close a region is to the facility that produces acetic acid. In 2025, there is an emerging trend towards regional supply chains (especially Southeast Asia and the Middle East) that have shortened supply chains with regional production facilities and transportation. Regional production, as well as shorter transport distances, will reduce both increasing transportation costs and reducing the carbon footprint related to logistics.
Digitalization and Automation
The logistics industry, which includes the chemical sector, is integrating more digital technology. The use of real-time tracking systems, automated warehouses, and smart inventory management drive efficiencies throughout the supply chain by reducing human error and ensuring transparency in the delivery of goods.
Automation in the manufacturing and distribution process are also allowing companies to address labor shortages and increased regulatory expectations. Smart warehouses, for example, have also become essential to the safe handling of hazardous materials like acetic acid.
The effect of the political unrest in Nepal on the logistics of acetic acid
Disruption of cross-border trade
The political unrest in Nepal has recently disrupted trade with India. The unstable political climate in Nepal has caused protests and strikes that block supply routes, such as the Rupaidiha land port in Bahraich, that manages the movement of essential goods, like chemicals (such as acetic acid). Nearly 1,000 trucks have been stranded and are causing delays in the delivery of chemicals and other products.
The consequences of this disruption have extended beyond Nepal’s borders, adversely impacting neighboring countries that depend on stable raw material supplies. For instance, chemical manufacturing plants reliant on timely deliveries of acetic acid have been forced to halt operations temporarily, causing setbacks to local economies and adding cost pressures across affected supply chains.
Suspension of Industrial Activities
Several fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) companies, notably Dabur, have faced considerable setbacks due to factory closures and transportation disruptions. For instance, Dabur’s manufacturing unit in Birgunj, Nepal that supplies their products to Nepal and surrounding areas, has been greatly affected by the unrest. This has led to suspended operations, meaning lost production capacity, and factory workers face job uncertainty because strikes have forced companies to stop regular working shifts.
The overall economic instability in Nepal only worsens this situation and, as a result, many companies are reconsidering investments and operation plans. Furthermore, the lost production capacity has compounded difficulties for companies that use chemicals as inputs for their production, including acetic acid.
Economic Impact
The political instability in Nepal led to extensive damage to the economy. It is estimated that the total cost to the economy is in the region of INR 3 trillion, which is about Nepal’s total annual budget. Auto dealers as well have indicated their losses may reach INR 5 billion. There were also significant job losses for almost 10,000 workers, further adding to the economic crisis in Nepal.
The political instability had a spillover effect on the economies of neighboring countries, especially other countries that trade with and have business interests in Nepal. The disruption of critical supply chains has delayed production facilities throughout the region, hindering their ability to respond to market demand.
Challenges facing Acetic Acid market
Regulatory Challenges: The production of acetic acid is an area where producers must operate under strict obligations regarding environmental regulations, especially in Europe and North America. As the world continues to move towards more sustainable manufacturing, chemical producers are continually pursuing cleaner production alternatives, and the means for alternative production through bio-based acetic acid production are becoming more apparent with increasing pressure for greener manufacturing methods.
Market Volatility: Price fluctuations due to variable feedstock costs, political unrest, and supply disruptions from trade continue to present contender risks for the acetic acid market. Political unrest in Nepal in 2022 demonstrated how quickly trade routes can become disrupted and unpredictable, thus magnifying risk to the market. Stakeholders in the acetic acid industry will have to commit to flexible approaches to respond to risks while managing stable supply chains.
Technological Innovations: Emerging production technologies and logistics innovations will likely manage many challenges in the acetic acid market. Automation technology and digital integration and bio-sourced production alternatives are extending new opportunities in cost management and environmental sustainability. Ongoing investments in innovation and research and development will be paramount for producers of acetic acid to remain positioned to meet emerging (demand challenges) and customer’s sustainability agenda.
Navigating Changing Market dynamics
In 2025, the acetic acid market is undergoing shifts in production, demand, and supply chains. The implementation of new technologies in production methods and adoption of sustainable practices will pave the way for the industry to adapt to its future. Conversely, events during the recent political unrest in Nepal have reminded us how fragile supply chains can be. Disruption in Nepal has led to significant financial losses that depended on the ability to supply goods, especially in chemical industries.
Post-pandemic, leaders in the acetic acid industry should utilize flexible approaches to navigate the risks of political disruption, price volatility, and regulatory constraints. With investments in technological innovations and cooperation at the regional level, the acetic acid industry is hoping to continue to meet global demand for acetic acid in a sustainable and efficient manner.